


| Title: | Location | K-4 | 5-8 | 9-12 | Description | Discipline |
| Octave Illusion | SoundGarden | In which ear do you hear the high and low tones? |
TIP: although you can use the speakers on your multimedia computer, a Make sure the volume isn't too loud!
This illusion uses two tones an octave apart. One is high, the other low. When played together your brain does something unexpected.

 (06") – listen to the high-low sine wave tones, left ear only.
(06") – listen to the high-low sine wave tones, left ear only. (06") – listen to the low-high sine wave tones, right ear only.
(06") – listen to the low-high sine wave tones, right ear only.- What do you think will happen when you listen to them at the same time?
 (30") – listen to the sine wave tones combined in both ears, 240 beats per minute.
(30") – listen to the sine wave tones combined in both ears, 240 beats per minute.
Did you hear the high tone in both or one ear? What about the low tone? What's happening?
Many people hear the low tone only in their left ear and the high tone only in their right ear. Some people hear the exact opposite. Most people perceive a sense of back-and-forth motion between their ears and perceive no change when they switch headphones!

People have reported hearing some surprising things, like an additional "phantom" tone alternating between the high or the low tone!
What's the point?
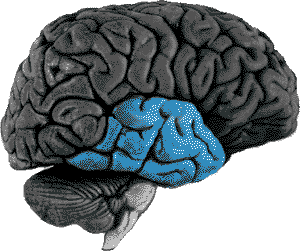
Human brain with temporal lobe highlighted.
Did you know that you process most of your auditory information in the temporal lobes of your brain? That's right and you actually have two of them, one on each side brain, close to your ears. [ They're not really blue – they're grey, we just did that to make it easier to point out. ]
Anyway, the point here is that your brain has two separate mechanisms for sound perception:
- one for perceiving sound frequency,
- the other for perceiving sound direction.
The tones reach both ears at the same time when you use headphones, but since the order constantly changes in each ear, your brain is "fooled" into perceiving the tones as moving back and forth.
At some point lift a single headphone off of your ear. What happens?
What happens when you switch the headphones?
What other experiments could you try?
Just for Fun!
What happens if you use different sounds, for example a piano sound?
 (30") – listen to piano tones, 240 beats per minute.
(30") – listen to piano tones, 240 beats per minute.- Or a hand drum?
 (30") – listen to hand drum tones, 240 beats per minute.
(30") – listen to hand drum tones, 240 beats per minute.
What can you conclude about the effect of timbre on this illusion? What other experiments could you try?
What will happen if you slow down the tones?
 (30") – listen to slower sine wave tones, 120 beats per minute.
(30") – listen to slower sine wave tones, 120 beats per minute. (30") – listen to slower piano tones, 120 beats per minute.
(30") – listen to slower piano tones, 120 beats per minute. (30") – listen to slower hand drum tones, 120 beats per minute.
(30") – listen to slower hand drum tones, 120 beats per minute.
What can you conclude about the effect of speed on this illusion? What other experiments could you try?
"Between the idea
And the reality
Between the motion
And the act
Falls the shadow."
– T. S. Eliot
Send your comments to: webteam@cafemuse.com
© 1996 – 2013 NewWorldView, All Rights Reserved.